A Sales Director can report to various titles including the C-Suite titles such as CEO and CRO and sales leadership titles such as VP of Sales. However, there are many other titles we’ll explore below.
What Is a Sales Director
A Sales Director, also referred to as a Director of Sales, is a high-ranking executive responsible for the strategic leadership and management of a company’s sales operations. They are tasked with developing and executing a cohesive sales strategy to drive business growth and increase profit.
Key responsibilities of a Sales Director include:
- Strategic Planning: Setting short-term and long-term sales targets and ensuring alignment with the company’s goals.
- Leadership: Leading, motivating, and managing the sales team, often including sales managers and representatives, to achieve sales objectives.
- Sales Training: Organizing training programs to enhance the team’s skills and knowledge, which is crucial for improving sales performance.
- Decision-Making: Using key insights from sales data and market analysis to make informed business decisions and adjust strategies accordingly.
The role demands strong soft skills, such as communication, problem-solving, and time management, enabling a Sales Director to effectively lead their team and interface with other departments. They are expected to understand the nuances of the market and customer needs, tailoring strategies to suit those requirements.
Their performance is often evaluated on their ability to meet and exceed sales targets, expand market share, and contribute to the company’s profitability. A Sales Director’s ability to synthesize sales performance data into action plans is crucial for sustained business success.
A successful Sales Director commands the respect of their team through transparent leadership and decision-making. By fostering a culture of achievement and accountability, they ensure that the sales department functions as a robust, revenue-generating arm of the organization.
Titles That a Sales Director Reports To
A Sales Director is a crucial link in the business hierarchy, responsible for overseeing sales operations, meeting revenue targets, and managing the sales team.
They report to senior executive titles within the organization, which vary depending on the company’s size, structure, and industry.
These titles embody individuals who generally oversee the sales director’s contributions to the company’s sales figures, sales strategies, and overall performance.
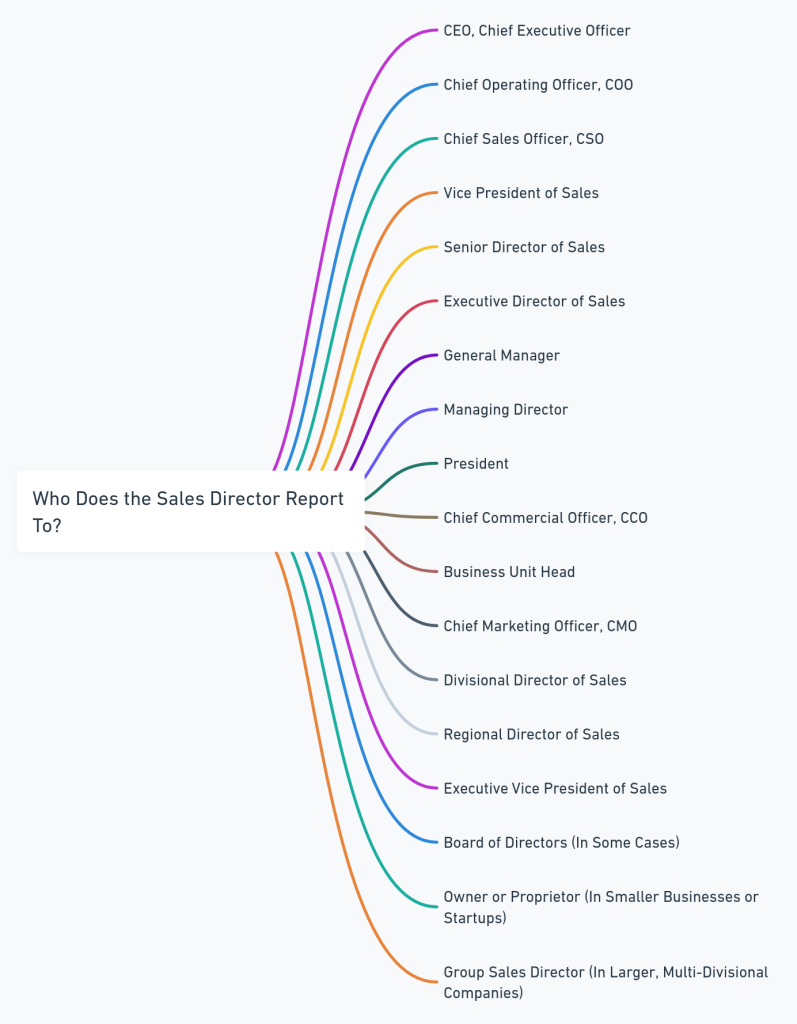
CEO, Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
The CEO holds the highest position in a company and monitors the overall performance, including the sales figures and strategies set out by the Sales Director to ensure alignment with the company’s objectives.
Chief Operating Officer (COO)
COOs often manage operational details, which may include the sales team’s productivity and the effectiveness of sales operations in driving business growth.
Chief Sales Officer (CSO)
The CSO directly oversees all sales-related aspects, including the sales pipeline, sales goals, and the efficacy of sales processes to optimize revenue and conversion rates.
Vice President of Sales
They supervise sales performance against quotas, guide sales strategies, and report on trends that could affect the sales cycle or targets. Hiring a VP of sales should not be taken lightly.
Senior Director of Sales
Senior Directors often have a hands-on role in managing sales operations and analyze sales reports to advise on improving sales numbers and market share.
Executive Director of Sales
Executive Directors focus on strategic directions for the sales team, ensuring that sales tactics align with the company’s long-term vision and relevant industry benchmarks.
General Manager
General Managers might receive reports on sales to understand how sales impact the larger operational context of the business unit.
Managing Director
A Managing Director evaluates comprehensive sales data, including sales forecasts and sales activity reports, to make decisions that affect the company’s direction.
President
The President monitors overall sales health through key performance indicators such as win rates and sales cycle lengths, using this data to shape business strategies.
Chief Commercial Officer (CCO)
The CCO steers the company’s commercial strategy, focusing on sales volume in addition to overseeing marketing efforts and customer acquisition processes.
Business Unit Head
Heads of business units assess sales reports specific to their division, tracking monthly and quarterly sales results and revenue by salesperson.
Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
The CMO integrates sales metrics with marketing efforts, examining how lead generation and brand positioning impact the sales funnel.
Divisional Director of Sales
Divisional Directors oversee the sales operations within their specific division, making sure the sales pipeline aligns with the company’s overall objectives.
Regional Director of Sales
Regional Directors manage sales within their geographical area and analyze localized sales strategies and results, considering response times and churned customers.
Executive Vice President of Sales
Responsible for a top-level view of sales effectiveness they examine everything from sales techniques to onboarding and sales training efficacy.
Board of Directors (In Some Cases)
The Board sometimes participates in overseeing sales operations, particularly in relation to how sales outcomes influence overall corporate governance.
Owner or Proprietor (In Smaller Businesses or Startups)
Small business owners or startup proprietors may directly oversee sales operations, including daily sales activity, due to the more hands-on nature of their roles.
Group Sales Director (In Larger, Multi-Divisional Companies)
In complex organizational structures, the Group Sales Director might oversee multiple sales directors, examining overarching trends and sales performance across divisions.
Reach out to a seasoned sales recruiting firm to help with placement for any sales director position you may need.